In today’s digital landscape, protecting your privacy isn’t just a technical concern, it’s a human rights issue. With a background in law and a strong interest in digital rights and security, I believe privacy should be a right that everyone can understand and protect, regardless of their technical background.
This newsletter is designed to teach everyday users simple, practical steps to better protect their digital footprint and regain a bit more control online. Along the way, it explains important concepts so we can better understand how our data moves and how to keep it safe.
Private Messaging Apps
How They Work, Why They Matter, and How to Choose One
What is private messaging?
Private messaging means having conversations that only you and the intended recipients can read, and no one else. This level of protection is made possible through end-to-end encryption (E2EE).
End-to-end encryption means:
Your messages are scrambled (encrypted) on your device before they’re sent.
Only the intended recipient’s device can unscramble (decrypt) them.
Not even the app’s company, your internet service provider (ISP), network administrators, hackers, or the government can read your messages while they’re in transit or stored on servers.
In short, private messaging ensures your conversations stay between you and the people you trust.
💡 Pro Tip: Always check if your messaging app uses end-to-end encryption by default. Some apps offer it only for "secret" or special chats.
What happens when you send a message without E2EE?
When you send a message through a typical messaging app without end-to-end encryption, here’s what usually happens:
Your message leaves your device in readable form. The message is sent unencrypted or only encrypted between you and the app’s server.
Message travels to the app’s central server. This server acts like a middleman, receiving your message.
The server reads and processes your message. Because it’s either unencrypted or only encrypted in transit (like with HTTPS), the server can decrypt and view the message content once it arrives.
The server sends the message to the recipient’s device. The message may be encrypted again during this leg of the journey, but the server still has full access to the content.
The recipient’s device receives and displays the message.
Implications: Because the app’s servers can read your messages, they can potentially store, scan, or share your conversations. This creates risks from data breaches, government requests, or misuse by the app company.
What happens when you send a message with E2EE?
When you send a message through a private messaging app with end-to-end encryption, here’s what usually happens:
Your message is encrypted on your device before sending. Your device scrambles the message content into ciphertext using a unique encryption key. This key is known only to your device and the recipient’s device.
The encrypted message travels to the app’s server. The server only sees unreadable ciphertext. It cannot decrypt or read the message.
The server forwards the encrypted message to the recipient’s device. Because it can’t read the message, the server cannot scan, store, or share the contents.
The recipient’s device decrypts the message locally. Using their private key, the recipient’s device unscrambles the ciphertext back into readable text.
The recipient reads the decrypted message on their device.
Implications: Because messages are encrypted from end to end, no third party (not even the app itself) can read them. This protects you from surveillance, hacking, and corporate misuse.
💡 Pro Tip: End-to-end encryption relies on secret digital keys stored on your devices. If someone gains access to your device through weak passwords or outdated software, they could potentially access those keys and read your messages. Use strong passwords and keep software up to date to stay secure.
⚠️ Note: End-to-end encryption (E2EE) protects the content of your messages but not the metadata (i.e., who you're contacting, when, or from where). That’s why it's important to combine E2EE with other privacy tools: encrypted DNS (to prevent DNS-based tracking), VPNs (to hide your IP address), and MAC address randomization (to prevent device tracking on local networks).
Why should you care?
Because your messages often reveal more than you think. Without end-to-end encryption and other privacy protections, your private conversations can be:
intercepted or read by the app’s company, your ISP, network administrators, hackers, or the government
Scanned, stored, or analyzed by companies behind the app
Used to identify you (even if you use a pseudonym)
Collected to build behavioral profiles based on who you talk to, when, and how often
Shared with third parties, including law enforcement or marketing firms, sometimes without your knowledge
Using a secure messaging app helps shield you from that kind of exposure. It’s one of the most effective ways to keep your conversations private, protect your identity, and communicate freely without fear of surveillance or misuse.
💡 Pro Tip: The more mainstream encrypted apps become, the harder it is for surveillance agencies to justify mass interception or weaken encryption standards. Widespread use normalizes privacy and removes the stigma that encryption is only for people with something to hide.
Okay, I'm in! How do I choose a private messaging app?
Some messaging apps claim to protect your privacy but still collect and share your usage data behind the scenes. Others display ads, have weak default security settings, or are owned by companies with questionable privacy practices.
What are key features of a secure private messaging app?
🧹 Open Source: Is the app’s code code publicly available for independent security audits?
🗝️ End-to-End Encryption (E2EE): Are your messages encrypted on your device and only readable by the intended recipient and not the app’s servers?
👁️🗨️ Encrypted Calls & Media: Does the app encrypt not just text messages, but also voice calls, video chats, images, and other files?
📔 Encrypted Contacts: Does the app protect your contact list or does it upload and store it in plain text on its servers?
🥷 Secure if Keys Stolen: If your encryption key or device is compromised, can an attacker read your past messages or impersonate you? Or does it include protections like forward secrecy (which ensures older messages can’t be decrypted even if current keys are exposed), key rotation (which regularly updates encryption keys to limit exposure), and account lockout (which prevents unauthorized access if someone tries to hijack your identity)?
📉 Minimal Metadata: Does the app avoid logging who you talk to, when, and how often, or does it at least limit that data?
🙈 No Personal Info Required: Can you sign up without giving a phone number or revealing your identity?
⚖️ Privacy-Friendly Jurisdiction: Is the company based in countries with strong privacy laws and minimal surveillance mandates?
Comparison Chart of Well-Known Private Messaging Apps
The chart below compares six well-known Private Messaging apps— Session, Signal, Wire, Zangi, WhatsApp, and Telegram—based on the criteria outlined above.
The best choice for you will depend on your desired level of privacy, security, and anonymity
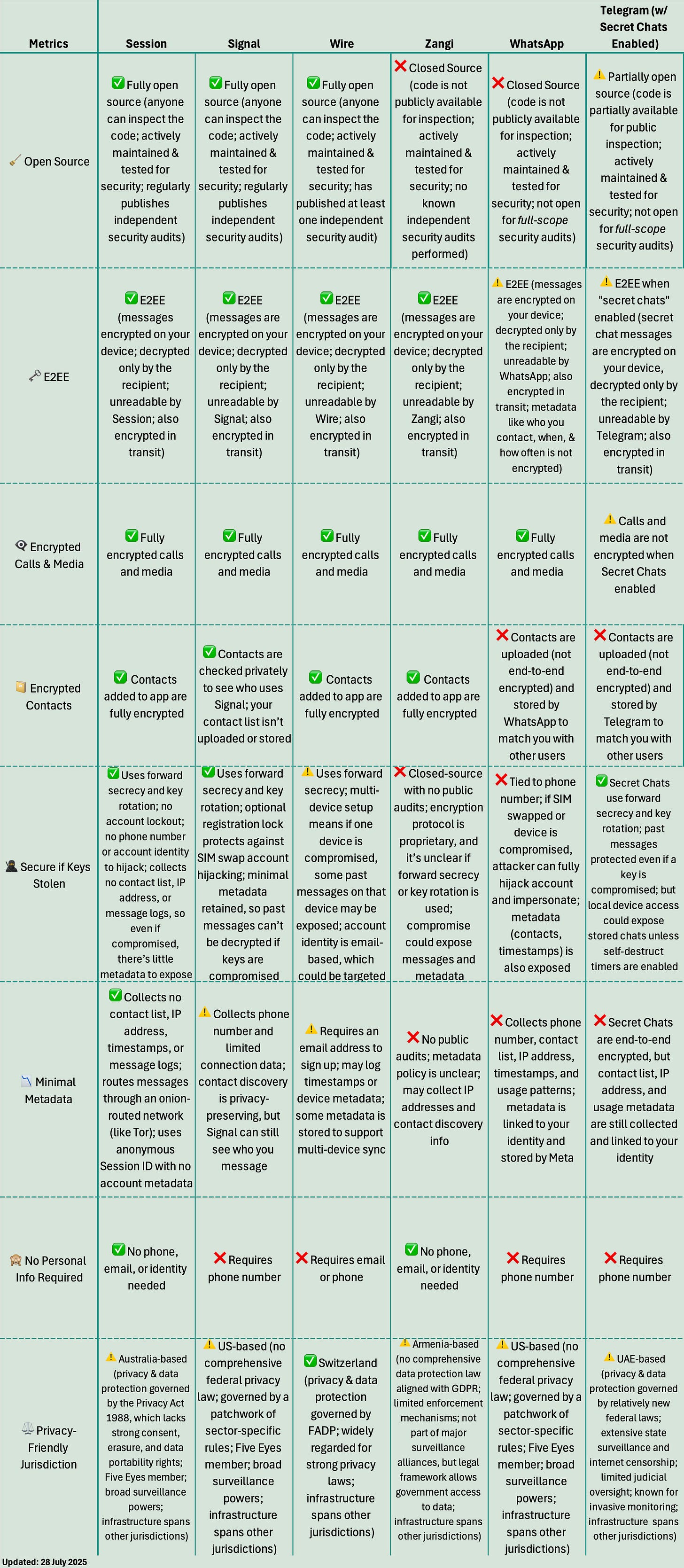
💡 Pro Tip: If a messaging app is closed source or only partially open source, it’s difficult to independently verify whether it truly uses end-to-end encryption as claimed. Unless the full source code is made available to auditors or the public, you’re relying solely on the company’s word, without a transparent way to confirm how your messages are actually encrypted or handled.
💡 Pro Tip: When signing up for online services, consider using email aliases or forwarding addresses. This helps prevent spam, phishing, and long-term tracking tied to a single email identity.
How to Get Started
Step 1: Choose your preferred provider.
Step 2: Install the app on your device and follow their setup guide for your operating system (OS).
Step 3: Open the app and complete the initial setup.
That’s it. If you’ve chosen the right app, you’re now communicating over a private, encrypted channel that shields your conversations from most forms of surveillance and interception.
An Important Note on Jurisdiction
Where a privacy service is based and where it operates its servers can significantly affect how your data is managed.
Some countries have strong privacy laws that require court orders or due process before authorities can access user data. Others are part of intelligence-sharing alliances or have laws that allow broad surveillance or secret government demands. This means even trustworthy services may be forced to collect or share your information. Sometimes without telling you.
Some privacy-focused companies, like Mullvad, go a step further by carefully choosing where their servers are located. They may avoid placing servers in countries with weak privacy laws, mass surveillance programs, or aggressive data retention mandates. Others operate globally without these precautions, meaning your data could pass through and be stored in high-risk jurisdictions, even if the company itself is based in a privacy-friendly country.
When evaluating a service, it’s worth considering:
Where the company is headquartered
Where it runs its servers
Whether it owns and controls its infrastructure or relies on third-party hosting
For more detailed information on data protection laws by country, visit DLA Piper’s comprehensive guide, which covers over 160 jurisdictions worldwide. The platform offers an interactive heatmap and in-depth summaries of each country’s privacy laws.
💡 Pro Tip: Where a service is based matters, but strong privacy protections—like open-source code and end-to-end encryption—can reduce risks even in less private jurisdictions.
A detailed, easy-to-use Digital Privacy Log now accompanies this newsletter. It’s designed to help you keep track of the privacy tools you’ve installed, document your setup across devices, and securely store recovery codes, configuration notes, and other key settings all in one place.
Stay tuned for Encrypted Email Services—How They Work, Why They Matter, and How to Choose One
Questions or feedback? Drop them below or send a private message.
#PrivateMessaging #Encryption #Session #Signal #DigitalRights #DigitalPrivacy #DigitalSecurity #DigitalFreedom #HumanRights
Session and Signal Messenger are notable private messaging apps. Neither sponsor this article, and each offers tools designed to help create a safer, more private internet.
If you’re interested, I encourage you to explore these options and choose the one that best fits your needs.
Newsletter Summary: Everyday Digital Privacy
This newsletter shares simple steps everyday users can take to strengthen our digital privacy, security, and anonymity:
🔒 Encrypting Your DNS Traffic — Learn how DNS requests reveal which websites you're trying to visit and how to encrypt them using services like Cloudflare, Quad9, Mullvad, and NextDNS.
🛡️ Hiding Your IP Address with a VPN — Understand what an IP address is, how your IP address exposes your location and identity, and how a trustworthy VPN like Mullvad VPN, Proton VPN, Riseup VPN, and Windscribe can encrypt all your traffic and hide where you’re connecting from.
📡 Hiding Your MAC Address — Discover how your devices' unique hardware IDs can be tracked by Wi-Fi networks (even when they're not online) and how to enable MAC address to limit passive tracking.
🌐 Privacy-Focused Browsers — Explore how your choice of browser impacts your online privacy, why mainstream browsers often collect extensive data, and how privacy-focused browsers like Mullvad, Tor, Firefox, and Brave can help block trackers, fingerprinting, and unwanted data collection.
💬 Private Messaging Apps — Understand what makes a messaging app truly private, how end-to-end encryption protects your conversations, why metadata still matters, and how to choose secure apps like Session or Signal that safeguard your communications from surveillance and hacking.
📧 Encrypted Email Services — Find out why email is one of the least private forms of communication by default, how end-to-end encryption works, and how to choose secure email providers like Posteo, Proton Mail, and Tuta that protect your messages (even from themselves).
💾 Secure Cloud Storage & File Sharing — Learn why mainstream cloud services leave your files exposed, how end-to-end encrypted storage tools keep your documents private, and how to share files securely using services like Cryptomator, Filen, Proton Drive, Tresorit or Sync.
🗝️ Encrypted Password Managers — Learn how password managers work, what makes one secure, and how to choose tools that use end-to-end encryption and zero-knowledge architecture. Compare options like KeePassXC, LessPass, Proton Pass, and Bitwarden to find the right balance of privacy, usability, and control.
🔎 Private Search Engines — Learn how search engines track what you’re curious about, how that data is used to profile you, and how private alternatives like Startpage, Mojeek, Brave Search, Qwant, and DuckDuckGo let you search the web without being watched, logged, or targeted.
✉️ Email Alias Services — Learn how alias tools like SimpleLogin, addy.io, Firefox Relay, DuckDuckGo, and Apple Hide My Email protect your real address from spam, tracking, and data leaks by letting you create unique, disposable email addresses for each site or app.






