Secure Cloud Storage & File Sharing
How It Works, Why It Matters, and Tools to Help You Take Control
In today’s digital landscape, protecting your privacy isn’t just a technical concern, it’s a human rights issue. With a background in law and a strong interest in digital rights and security, I believe privacy should be a right that everyone can understand and protect, regardless of their technical background.
This newsletter is designed to teach everyday users simple, practical steps to better protect their digital footprint and regain a bit more control online. Along the way, it explains important concepts so we can better understand how our data moves and how to keep it safe.
Secure Cloud Storage & File Sharing
How It Works, Why It Matters, and Tools to Help You Take Control
What is secure cloud storage and file sharing?
Secure cloud storage and file sharing means keeping your files safe and private when stored online or shared with others. Unlike traditional cloud storage, which may expose your data to unauthorized access, secure solutions use strong encryption and privacy protections so that only you and the people you choose can access your content.
There are three main layers of protection:
Encryption in transit: Your files are encrypted while being uploaded or downloaded, which protects them from interception during transfer. However, once they reach the provider's servers, they’re often decrypted. This means the provider may be able to access them, comply with government requests, or be vulnerable in a breach.
Encryption at rest: Files stored on the provider’s servers are encrypted to guard against physical theft or unauthorized access to the storage system. But if the provider holds the encryption keys, they can still access your data and may be required to turn it over to third parties.
End-to-end encryption (E2EE): Your files are encrypted on your device before upload and decrypted only on the recipient’s device (or yours upon retrieval). The provider never sees the unencrypted files and doesn’t have the keys, so even if their systems are hacked or subpoenaed, your data remains private.
💡 Pro Tip: Popular cloud services like Google Drive, Dropbox, or OneDrive generally do not offer true end-to-end encryption. If privacy matters, look for providers that encrypt your data before it leaves your device.
What happens when you use cloud storage with encryption at rest and in transit?
When you use a typical cloud storage service that supports encryption at rest and in transit, here’s what usually happens:
Your file leaves your device in readable form. It might be encrypted in transit using HTTPS, which protects it from being intercepted on the way, but the content can still be accessed once it reaches the provider’s servers.
The file is delivered to the provider’s server, where it’s stored with encryption at rest. This protects the file from physical theft or disk-level attacks, but the provider controls the encryption keys and can decrypt and read the contents.
The provider may scan or process your files. Many services automatically analyze stored content for indexing, malware detection, or personalized features, sometimes including targeted advertising or behavioral analytics.
When you share a file, the provider manages access permissions. Even if links or user access are restricted, the provider still holds the encryption keys and can view the shared content.
Implications: Your files are vulnerable to unauthorized access, government surveillance or legal demands, and data breaches. You’re relying entirely on the provider’s security practices and policies (not encryption) to keep your data private.
What happens when you use cloud storage with E2EE?
When you use a cloud storage service with E2EE:
Your file is encrypted on your device before upload. The encryption process uses keys that only you control, so the content is protected before it ever leaves your device.
The encrypted file is stored on the provider’s servers. Because the provider never sees your encryption keys, they can’t decrypt or read the file—they only store scrambled, unreadable data.
When you share a file, the recipient receives an encrypted version. Only they can decrypt it using their own private keys, ensuring the provider can’t access the shared content.
The file remains encrypted throughout its entire journey (i.e., in transit, at rest, and during sharing). At no point does the provider gain access to the readable version.
The recipient decrypts the file locally on their device. Using their private key, they convert the ciphertext back into its original form for viewing.
Implications: Even if the provider is hacked or compelled to disclose data, your files remain protected and unreadable without your encryption keys. This significantly reduces risks of surveillance, breaches, and unauthorized data access.
💡 Pro Tip: Some cloud services use end-to-end encryption, meaning only your devices hold the keys to unlock your files. But if someone gains access to your device through weak passwords, outdated software, or a compromised account, they may also gain access to your encrypted data. To stay protected, use strong, unique passwords, enable two-factor authentication, and keep your devices and software up to date.
Why should you care?
Because your cloud storage often holds private and valuable data, including:
Personal documents (IDs, tax records, contracts)
Photos and videos
Work files and sensitive projects
Password backups or security keys
Without strong encryption, this data can be:
Accessed by hackers if servers are breached
Viewed or scanned by cloud providers for profiling or advertising
Exposed in government surveillance or legal requests
Shared unintentionally if permissions are misconfigured
Using secure, encrypted cloud storage protects your digital life from these risks, keeping your data truly private and under your control.
Okay, I'm in! How do I choose a secure cloud storage service?
Some cloud storage providers claim to protect your privacy but still collect and share your usage data behind the scenes. Others may display ads, have weak default security settings, or be run by companies with questionable privacy practices.
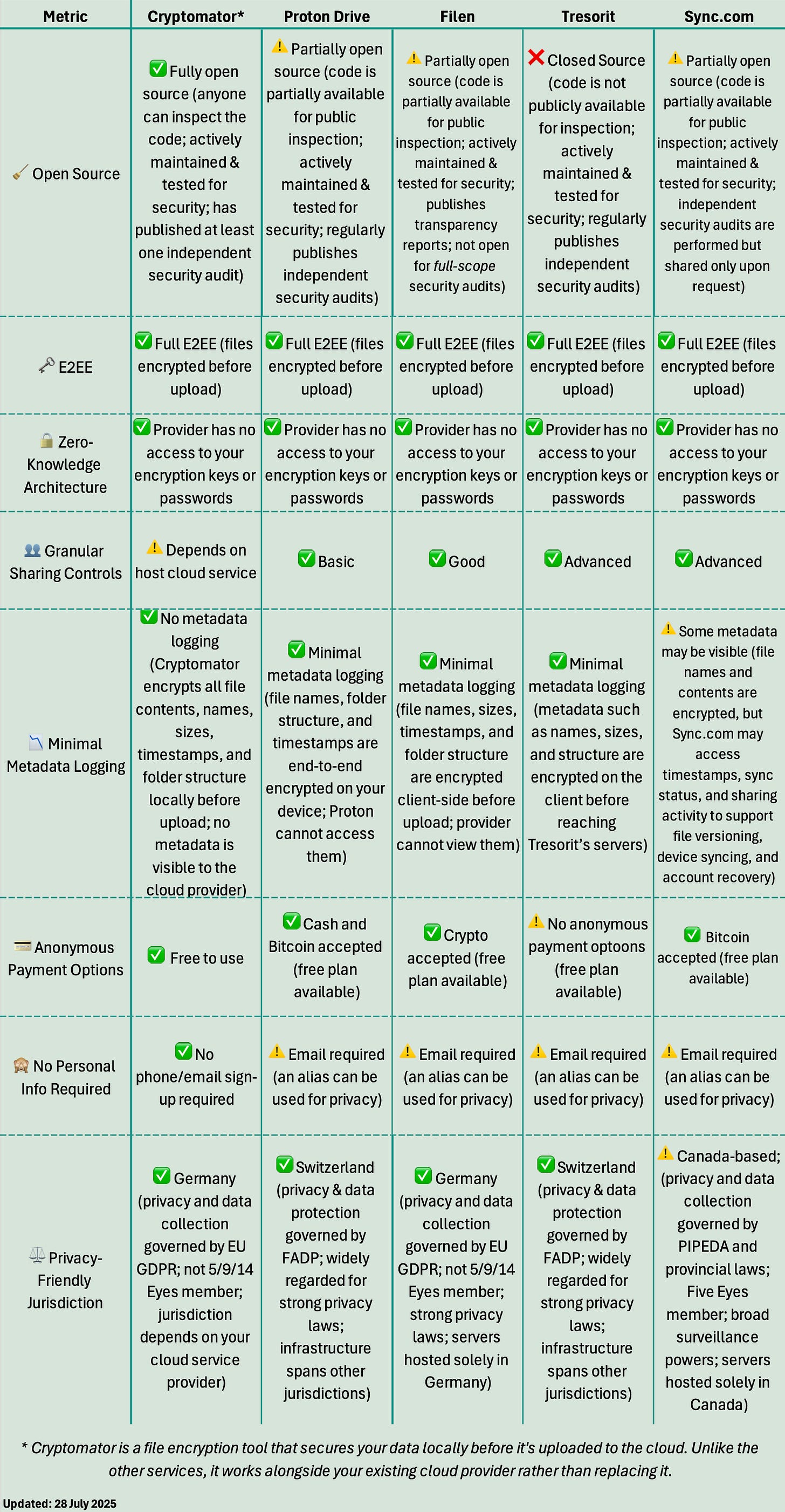
What are key features of a secure cloud storage service?
🧹 Open Source: Is the service’s code publicly available for independent security audits?
🗝️ End-to-End Encryption: Are files encrypted on your device before upload and only decrypted by intended recipients?
🔒 Zero-Knowledge Architecture: Does the provider have no access to your encryption keys or passwords?
👥 Granular Sharing Controls: Does the service let you control who can access, edit, or share your files?
📉 Minimal Metadata Logging: Does the provider limit what metadata it collects or retains about your files (e.g., file names, sizes, timestamps, folder structure, or sharing activity) and are those details encrypted client-side?
💳 Anonymous Payment Options: Does the service accept anonymous payments like cryptocurrency, gift cards, or even cash?
🙈 No Personal Info Required: Can you sign up without revealing your identity?
⚖️ Privacy-Friendly Jurisdiction: Is the provider based in countries with strong data protection and limited surveillance?
Comparison Chart of Well-Known Cloud Storage Providers
The chart below compares five well-known cloud storage providers— Cryptomator, Proton Drive, Filen, Tresorit, and Sync.com—based on the criteria outlined above.
The best choice for you will depend on your desired level of privacy, security, and anonymity
💡 Pro Tip: When signing up for online services, consider using email aliases or forwarding addresses. This helps prevent spam, phishing, and long-term tracking tied to a single email identity.
How to Get Started
🔐 How to Get Started with Cryptomator
Choose your operating system (Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, or iOS)
Download and install the app
Open Cryptomator and click “+ Add Vault” → “Create New Vault”
Choose a location for your vault. To use the cloud, save it inside your cloud sync folder (e.g., iCloud Drive, Dropbox, Google Drive)
Name your vault and click Create
Set a secure password and store your recovery key in a safe place
Unlock the vault. It will mount as a virtual drive on your system
Drag and drop files/folders into this mounted drive to encrypt them
After confirming everything has copied safely, you can delete the original unencrypted files from your computer or cloud drive to avoid duplicates
Your files are now encrypted and stored securely in your cloud service, protected by zero-knowledge encryption. This means even Cryptomator cannot access the contents of your files.
To access your files later, simply:
Open Cryptomator
Unlock the vault with your password
Access your encrypted files through the mounted drive
⚠️ Note: Cryptomator encrypts files before they’re uploaded to the cloud (e.g., Dropbox, Google Drive). It works alongside your existing cloud service.
📁 Filen
Visit https://filen.io/
Click Get Started Free
Create an account using an email address
Choose your operating system (Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, or iOS)
Download and install the app
Log in to your new account
Begin uploading files
Your files are now securely stored and protected by zero-knowledge encryption. This means even Filen cannot access the contents of your files.
🧪 Proton Drive
Visit https://proton.me/drive
Click Get Proton Drive
Under the "Proton Free" 5 GB plan, click sign-up free
Create an account using an email address
Use the web interface to upload files immediately
For mobile access, download the Proton Drive app on Android or iOS
Your files are now securely stored and protected by zero-knowledge encryption. This means even Proton cannot access the contents of your files.
🏢 Tresorit
Choose your device (Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, or iOS)
Download and install the app
Create an account using an email address
Begin uploading files
Your files are now securely stored and protected by zero-knowledge encryption. This means even Tresorit cannot access the contents of your files.
⚠️ Note: Tresorit is a business-grade zero-knowledge provider often used by legal, medical, and enterprise users.
🔄 Sync.com
Visit https://www.sync.com/
Create an account using an email address
Choose your platform (Windows, macOS, Android, or iOS)
Download and install the Sync app
Begin uploading files
Your files are now securely stored and protected by zero-knowledge encryption. This means even Sync.com cannot access the contents of your files.
⚠️ Note: Zero-knowledge encryption means the provider cannot access your files or passwords. When combined with end-to-end encryption (E2EE), this ensures only you and those you authorize can decrypt the data.
Can I not rely on Apple's Advanced Data Protection for iCloud?
Apple now offers end-to-end encryption (E2EE) for most iCloud data through a feature called Advanced Data Protection. When enabled, it ensures that only you can access your encrypted files. Not even Apple can decrypt them. That said, Mail, Contacts, and Calendar don’t support this kind of encryption.
And while this is a meaningful step forward for user privacy, it’s important to remember that technology companies around the world can face legal pressures from governments to introduce backdoors or provide access to user data.
For example, Apple recently removed its Advanced Data Protection tool in the UK after government concerns, highlighting how national security demands can impact privacy features even in major tech companies. (Source: The Guardian, Feb 2025)
To help protect your privacy further and guard against government overreach, you can use Advanced Data Protection alongside a tool like Cryptomator.
Cryptomator works seamlessly with iCloud Drive and adds client-side encryption, meaning your files are encrypted before they leave your device, and only you hold the keys.
To enable Advanced Data Protection:
Update your device to the latest version of iOS, iPadOS, or macOS.
Open Settings on your iPhone or iPad (or System Settings on Mac).
Tap your name to go to Apple ID.
Go to iCloud → Advanced Data Protection.
Follow the instructions to enable it. You’ll be asked to set up a recovery method, such as a trusted contact or a recovery key. Be sure to store your recovery key in a safe place.
⚠️ Note: Android devices rely on Google Drive for cloud storage by default, but Google Drive does not support end-to-end encryption (E2EE).
An Important Note on Jurisdiction
Where a privacy service is based and where it operates its servers can significantly affect how your data is managed.
Some countries have strong privacy laws that require court orders or due process before authorities can access user data. Others are part of intelligence-sharing alliances or have laws that allow broad surveillance or secret government demands. This means even trustworthy services may be forced to collect or share your information. Sometimes without telling you.
Some privacy-focused companies, like Mullvad, go a step further by carefully choosing where their servers are located. They may avoid placing servers in countries with weak privacy laws, mass surveillance programs, or aggressive data retention mandates. Others operate globally without these precautions, meaning your data could pass through and be stored in high-risk jurisdictions, even if the company itself is based in a privacy-friendly country.
When evaluating a service, it’s worth considering:
Where the company is headquartered
Where it runs its servers
Whether it owns and controls its infrastructure or relies on third-party hosting
For more detailed information on data protection laws by country, visit DLA Piper’s comprehensive guide, which covers over 160 jurisdictions worldwide. The platform offers an interactive heatmap and in-depth summaries of each country’s privacy laws.
💡 Pro Tip: Where a cloud service is based affects your privacy, especially in countries with broad surveillance powers. But features like zero-knowledge encryption, minimal metadata logging, and anonymous sign-up options can reduce those risks. Even if a provider is based in a less private jurisdiction, strong client-side protections can help keep your data secure.
💡 Pro Tip: If your preferred cloud storage provider offers a recovery email or key, make sure it's just as secure as your primary account. Weak recovery options are a common way attackers regain access. Consider printing or securely storing recovery keys offline.
A detailed, easy-to-use Digital Privacy Log now accompanies this newsletter. It’s designed to help you keep track of the privacy tools you’ve installed, document your setup across devices, and securely store recovery codes, configuration notes, and other key settings all in one place.
Stay tuned for Encrypted Password Managers—How They Work, Why They Matter, and How to Choose One
Questions or feedback? Drop them below or send a private message.
#SecureCloudStorage #Encryption #Cryptomator #Filen #ProtonDrive #Tresorit #Sync #DigitalRights #DigitalPrivacy #DigitalSecurity #DigitalFreedom #HumanRights
Cryptomator, Filen, Tresorit, and Sync.com offer encrypted cloud storage services designed to protect your privacy. None sponsor this article, and each provides tools to help you store and share files securely while maintaining control over your data.
If you’re interested, I encourage you to explore these options and choose the one that best fits your needs.
Newsletter Summary: Everyday Digital Privacy
This newsletter shares simple steps everyday users can take to strengthen our digital privacy, security, and anonymity:
🔒 Encrypting Your DNS Traffic — Learn how DNS requests reveal which websites you're trying to visit and how to encrypt them using services like Cloudflare, Quad9, Mullvad, and NextDNS.
🛡️ Hiding Your IP Address with a VPN — Understand what an IP address is, how your IP address exposes your location and identity, and how a trustworthy VPN like Mullvad VPN, Proton VPN, Riseup VPN, and Windscribe can encrypt all your traffic and hide where you’re connecting from.
📡 Hiding Your MAC Address — Discover how your devices' unique hardware IDs can be tracked by Wi-Fi networks (even when they're not online) and how to enable MAC address to limit passive tracking.
🌐 Privacy-Focused Browsers — Explore how your choice of browser impacts your online privacy, why mainstream browsers often collect extensive data, and how privacy-focused browsers like Mullvad, Tor, Firefox, and Brave can help block trackers, fingerprinting, and unwanted data collection.
💬 Private Messaging Apps — Understand what makes a messaging app truly private, how end-to-end encryption protects your conversations, why metadata still matters, and how to choose secure apps like Session or Signal that safeguard your communications from surveillance and hacking.
📧 Encrypted Email Services — Find out why email is one of the least private forms of communication by default, how end-to-end encryption works, and how to choose secure email providers like Posteo, Proton Mail, and Tuta that protect your messages (even from themselves).
💾 Secure Cloud Storage & File Sharing — Learn why mainstream cloud services leave your files exposed, how end-to-end encrypted storage tools keep your documents private, and how to share files securely using services like Cryptomator, Filen, Proton Drive, Tresorit or Sync.
🗝️ Encrypted Password Managers — Learn how password managers work, what makes one secure, and how to choose tools that use end-to-end encryption and zero-knowledge architecture. Compare options like KeePassXC, LessPass, Proton Pass, and Bitwarden to find the right balance of privacy, usability, and control.
🔎 Private Search Engines — Learn how search engines track what you’re curious about, how that data is used to profile you, and how private alternatives like Startpage, Mojeek, Brave Search, Qwant, and DuckDuckGo let you search the web without being watched, logged, or targeted.
✉️ Email Alias Services — Learn how alias tools like SimpleLogin, addy.io, Firefox Relay, DuckDuckGo, and Apple Hide My Email protect your real address from spam, tracking, and data leaks by letting you create unique, disposable email addresses for each site or app.




